<--!NoAds-->
English Studies at Ibn Zohr:
Professor Hassan Bouzidi’s Noticeboard

WELCOME NOTE

This page serves as a noticeboard for professor Bouzidi’s English studies groups and may hold information on the following: Handouts: no paper handouts will be used in class. All handouts will be distributed electronically via e-mail. Assignments: at the end of each class meeting, a workshop is organized and participants are given a home assignment on the subject discussed. Exam Dates are announced as soon as we get them, but the (Ibn Zohr) institutional website remains the official source of this type information. Extra Credit: students get extra credit (earn points) for attendance, active participation in class (moderating a discussion, for example), and in-class presentations. Assignments and projects are also rewarded. An open source reading List is provided for each subject to allow students to do some further reading before and after class meetings. When a website is deemed useful and can provide in-depth information on the topic at hand, it is included in the useful Links list. To receive professor Bouzidi’s notification e-mails, students are advised to register (find the student registration link at the bottom of this page).
Professor Hassan Bouzidi,
English Studies
Ibn Zohr University
Agadir – Morocco
APPLIED LINGUISTICS

Reading List
-
-
APPLIED
Applied Linguistics(Wikipedia)
-
ESP
English for Specific Purposes(Wikipedia)
English for Specific Purposes (An international Journal)
-
TEFL
English as a Foreign Language(Wikipedia)
-
PUBLIC SPEAKING

Class meetings
Public Speaking G3 & G4 (S3) class meetings take place at these times:
Tuesday | 16:00-18:00 | Room 5 Thursday | 16:00-18:00 | Room 7
NOTE: Class meetings have now started !
-
-
- MEETING ONE: Introductions

How to introduce yourself & others – November 19, 2014

How to Introduce Another Speaker in 3 Steps – November 4, 2011
- Workshop #1: “Introducing Yourself and Other People”
-
- MEETING TWO: Public speaking goals
- Goals: 1. Inform 2. Persuade 3. Entertain
- INFORM: This is about helping audience members acquire information that they do not already possess. Audience members can then use this information to understand something (e.g., speech on a new technology, speech on a new virus) or to perform a new task or improve their skills (e.g., how to swing a golf club, how to assemble a layer cake). The most important characteristic of informative topics is that the goal is to gain knowledge.
- PERSUADE: When we speak to persuade, we attempt to get listeners to embrace a point of view or to adopt a behavior that they would not have done otherwise. A persuasive speech can be distinguished from an informative speech by the fact that it includes a call for action for the audience to make some change in their behavior or thinking.
- ENTERTAIN: Whereas informative and persuasive speech making is focused on the end result of the speech process, entertainment speaking is focused on the theme and occasion of the speech. An entertaining speech can be either informative or persuasive at its root, but the context or theme of the speech requires speakers to think about the speech primarily in terms of audience enjoyment.

- Workshop #2: “Practice writing the three types of speech”
-
- MEETING Three: Public speaking Environment
- Environmental context refers to the physical space in which you’re speaking … can affect the degree to which the audience feels they can connect with you.
- Environment = (a) Where does public speaking take place (venue) and (b) What equipment/logistics are in place? (powerpoint#1 below)Why is listening difficult? (powerpoint#2 below)– Physical noises– Psychological noises– Physiological noises– Semantic noises

- Workshop #3: “The right public speaking venue”
-
- MEETING Four: Communication apprehension
- Speaking anxiety is a normal (psychological as well as physical) response to fear of being evaluated by the audience.Q: What can you do to overcome stage fright?A: Be well-prepared – Organize your speech; exercise (including facial exercises); eat well; sleep well; rehearse your speech at home (in front of a mirror/family members/friends); dress properly; be on time; talk to members of the audience prior to giving your speech; be positive.
- Myths about public speaking:– People who suffer from speech anxiety are sick.- Writing your speech word for word and memorizing it will help you deliver a great speech.– A joke is a good way to open your speech.- The audience is your enemy and is out to get you.- The first mistake you make means failure.

- Workshop #4: “Facing the audience”
- Reading: McCroskey, J. C., & Beatty, M. J. (1986). “Oral Communication Apprehension“. In W. H. Jones, J. M. Cheek, & S. R. Briggs (Eds.), Shyness: Perspectives on Research and Treatment (pp. 279-293). New York: Plenum Press.
-
-
- MEETING Five:Visual aids
- Types of Visual Aids:
- People, Maps, Objects
- Charts: -flow -tree -sequence -pictographs -flip
- Graphs: -pie -bar -line
- Photographs, Pictures, Diagrams, Sketches
- Projected Images: -overhead projectors -Powerpoint presentation -film
- Reasons to use Visual aids:
- Diverts audience’s attention “away from you”.
- Assists visual learners in understanding your topic.
- Holds audience’s attention.
- Allows the speaker to inject humor.
- Helps speaker gain credibility.
- Shows thorough preparation for the speech.
Tips for Effective Use of Visual aids:
Tip #1: Use a visual aid that will help your audience remember your message. If the prop ties in with the main idea, it can be very effective.
Tip #2: Visual aids must be simple or they may be (probably WILL be!) misunderstood.
Tip #3: Visual aids should be big enough so that everyone in the audience can see clearly.
Tip #4: Prepare well and practice before you use any visual aid. Many possible problems can come up in a presentation. Be sure you can handle any props easily before you get up to speak. Make sure the visual aids can be easily shown to the audience without distracting you or your listeners.
Tip #5: Don’t be afraid to use no visual aids at all! Instead of depending on a prop, you should depend on a strong message, well-organized and professionally presented. You already possess one of the best visual aids possible – your own self!

-
- Workshop #5: “Presentations: Visual aids”
- Meeting Six: Effective public speaking
_
__
_____
EFFECTIVE PUBLIC SPEAKING
_________________________
PRACTICE
Verbal delivery | Non-verbal delivery __________________________________
PREPARATION
Research | Organize | Support _____________________________________
FOUNDATIONS
Speech goal | Topic choice | Audience type ____________________________________________
- For more details see powerpoint #3 below
- Workshop #6: Impromptu speeches
- Meeting Seven: Three Modes of Persuasion
- Ethos: The appeal to the speaker’s or writer’s character or reputation.
-Share your experience/Research/Awards (But do not brag!)
-Establish a rapport with your audience (We trust people like us)
-Be honest
- Pathos: The appeal to emotion
– In the battle between reason and emotion, the latter usually wins (e.g. “advertising”)
- Logos: The appeal to reason
– Making inferences through deductive reasoning (e.g. “syllogism” = 2 premises + a conclusion).
- Workshop #7: Impromptu speeches

- Meeting Six: Effective public speaking
-
Reading List
Three Modes of Persuasion (Aristotle)
-
-
Handout
- Assignment #1Watch “Let the environment guide our development” TED speech by Johan Rockstrom.
- Write a critique of the speech using the “How to Study and Critique a Speech” handout above. Do make use of the transcript to help you analyze the speech.
- Assignment #2Watch “Quit Social Media” TED speech by Cal Newport. Rewrite the speech in your own words.
- Assignment #3Watch “Stop Wasting Time” TED speech by Jordan Peterson.Write a one paragraph summary of the the speech.
- Deadline: The deadline for submission of Public Speaking assignments is December 19, 2022!
- NOTE: Files should be sent by e-mail as a word document and clearly marked as Full-Name_Public speaking-assignment#1.docx. PDF files will not be processed. Late papers will be ignored. Refer to the paper submission guidelines at the bottom of this page.
-
-
-
International Public Speaking contest
-
The nationalPublic Speaking contest will take place at (at ENSET, Mohammedia) Saturday 23th March 2019 at 9am.
Candidates are advised to attend local and/or regional contests to understand the rules of public speaking as set by ESU. They also need to read the handbook carefully to be aware of what the adjudicators evaluate.
- This is the link to the handbook:IPS Competition Handbook 2019
- IPS Competition Handbook 2018
- This link takes you to last year’s IPS competition in London: IPS Competition 2017
-
-
-
Exam Format
Public Speaking oral Exam will take place in the form of a VIDEO recording not exceeding 5mns sent to professor Bouzidi via Google Drive !
-
Exam Schedule
Date: (Starting: January 12th)
Time: (…)
Venue: (…)
N.B.: Make sure your Full Name is attached to your file. Also make sure you set Google Drive permissions to “any one with the link”.
N.B: Receipt of videos is acknowledged here: Public Speaking. If you cannot see you name under the “Videos” column, just be patient! lt will eventually show as videos are being processed.
-
BUSINESS COMMUNICATION
Reading List
MEDIA STUDIES

Class meetings
Studies in Media (#2024S4)(G1 & G2) class meetings take place at these times:
Tuesday | 16:00-18:00 | Room 5 | G1
Thursday | 16:00-18:00 | Room 5 | G2
-
- MEETING One:IntroductionsWORKSHOP #1: “Introduction interviews”
- MEETING Two:Media StudiesDefinition: “A discipline and field of study that deals with the content, history and effects of mass media.”Key terms: “Media” or “The media” and also “mediums”, plural of “medium”. “mass media”, “media literacy”, “traditional media”, “modern media”, “media convergence”“audience”, “culture”, “communication”, “information”, “community”, “cyber-community”,
- A SHORT HISTORY MEDIA:
- [Thousands of years ago] Paintings on cave walls, [100BCE] Paper (papyrus) invented in China, [1500 years later] Printing (Johannes Gutenberg built the first printing press , mass production of books begins!), [17th century] First newspapers appeared. [1800s] High-speed rotary printing presses with railways making for wide distribution, [1835] Samuel Morse invented his code (Instant telegraphic contact) [1860s] The arrival of photography. [19th century] New technology allowed newspapers to print photographs, [1895] The Lumière brothers gave the first public demonstration of moving pictures in Paris, [1876] Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone. Instant two-way voice communication was possible, [1901] The Italian inventor Guglielmo Marconi developed wireless radio transmission, [1920] The first radio station was launched, [Eight years later] Pictures were added to sound. [1940s] sees widespread installation of televisions in homes.[1965] Two computers communicated with each other in a lab at MIT. Later refined to become ARPANET, adopted as a communication system by the U.S. military in 1969 and adapted commercially in [1974]. [1990] Tim Berners-Lee developed HTML. [The following year] The World Wide Web went into action. [by 1993] there were 600 websites and two million computers connected to the internet. [1998] Google search engine was born. In [2004] Facebook went online and the social networking phenomenon began. As of January [2020], there were more than 1.7 billion websites with about 140,000 new ones created daily.A Short History of MediaWORKSHOP #2: Consider the short history of Media above in terms of “media convergence”.
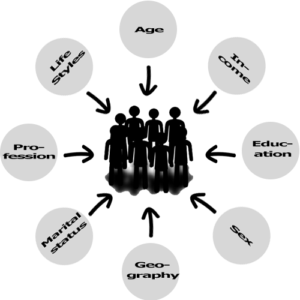
- MEETING Three:AudienceDefinition: “Total number of readers, listeners, or viewers reached by a particular medium”. As few as one person reading a magazine and as many as one billion watching the world cup.Key words: audience, audience segment, audience research, audience engagement, audience expectations (vague), audience foreknowledge (definite), audience identification, target audience, broad audience, niche audience, lay people, experts, eyeballs, demographics, psychometrics (e.g aspirer)Audience research: A major part of any media company’s work. Research conducted on specific audience (people) segments to obtain information about them.“Demographics” : Collection and study of data regarding the general characteristics of specific populations.

Graph 2: “Demographics”
Potential audience letter code:
A Top management, bankers, lawyers, doctors B Middle management, teachers C1 Office supervisors, junior managers, nurses, clerical staff C2 Skilled workers, tradespersons (white collar) D Semi-skilled & unskilled (blue collar) E Unemployed, students, pensioners, casual workers
Marketing:
- posters
- Ads
- Promotional interviews (e.g stars appearing on chat shows)
- Tie-in campaigns (e.g a blockbuster movie using McDonalds meals)
- Merchandising (T-shirts, key rings)
- Word-of-mouth (Informal way in which media products become known by audiences)
Counting an audience:
Film: Box office receipts Print: Circulation Radio/TV: Listening/viewing figures/ratings Internet: Hit rate/number of visitors
WORKSHOP #3: “All media are made with an audience in mind”. Discuss.
Consider the intended audience for the following mediums:
- “Animal farm” by George Orwell
- Your End-of term paper
- Sara’s diary
- MEETING FOUR: MEDIA TECHNOLOGIESDefinition: “Forms of mediation between producer and consumer. Key words: traditional media, one-to-one (e.g landline telephone), modern media, one-to-many (e.g. newspaper), audio recording (microphones/loudspeakers), Film (dubbing, subtitles), TV & Radio (frequency bands), analog (nondigital), computer/video/console game, mouse, console, joystick, digital, interactive, website (bandwidth/connection/optic fibre/streaming), cyborg (part biology and part technology!), touch screen, mobile/smart phone,
- Theories:(1) “Technological determinism” (Marshal McLuhan)Technologies determine societies (e.g. notions of time & space). The message is the medium.Further reading: “Media Technologies“(2) “Social constructivism” (Raymond Williams). Societies/cultures determine technologies. Power relations support dominant ideologies.

Table 4.1 : Characteristics of Various Mediums: Yes/No- WORKSHOP #4:Consider the limitations of various media in Table 4.1 above.
- MEETING FIVE: MEDIA EFFECTS
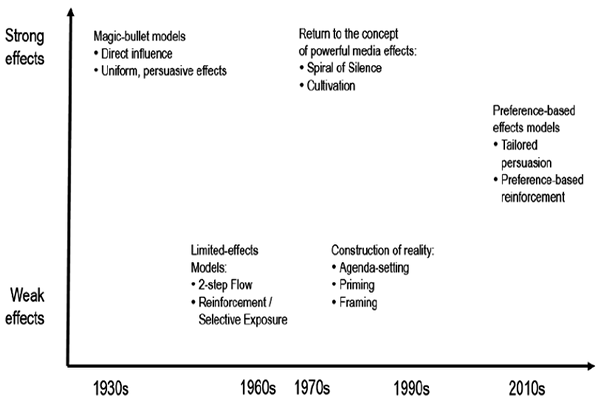
- Definition: “Media exposure impacts audiences in different (positive and negative) ways “Key words: Direct, Indirect, Encoding-decoding, Agenda setting, Audience as a commodity, Audience flow, Audience polarization, reinforcement, Conservative/moralist decision making, Consumer culture creation and reinforcement, Cultivation, Cultural imperialism, Culture of narcissism, Disinhibition, Disposition altering, Empathy activation, Excitation transfer, Global village, Gratification seeking, Gravitation Hegemony, Heuristic (not systematic) processing, Hidden persuaders, Homogenization, Imitation, Information flow, Information seeking, Integrated response, Interpretation by social class, Interpretive resistance, Knowledge gap, Levels of processing, Limited capacity information processing, Media entertainment, Media dependency, Medium as message, Message construction, Mood management, News factory, News frame creation, News selection, Perception, Power elite, Priming, Principled reasoning, Pseudo-events blur reality, Psychodynamics, Psychological conditioning, Reasoned action, Reception, Selective exposure, Selective gatekeeping, Selective perception, Semiotic interpretations, Social cognitions, Social construction of meaning, Social construction of media technologies, Social identity, Social learning, Social norms, Sociology of news, Spiral of silence, Trivialization of public life, VideomalaiseTheories:(1) The hypodermic needle: 1920s/1930s Also referred to as “Total effects model” and is still quoted in “moral panics”. Audiences passively receive (and make no attempt to process or challenge) information. Experience, intelligence and opinion of individuals is irrelevant.(2) Two-step flow: 1940s Also referred to as “Limited effects paradigm” Information is mediated by “opinion leaders” who filter it to their less active “associates”. (3) Uses and gratifications: 1960s Individuals consume texts for different reasons. Diversion (escapism), Personal relationships, Personal ID (finding yourself in texts), Surveillance (useful information for practical purposes), (4) Reception theory: 1980s/1990s There may be more than one reading (decoding/interpretation) of the text, Preference-based (tailored persuasion) 2010s

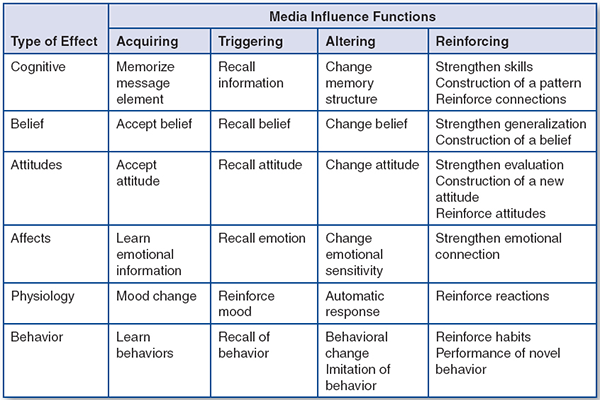
Table 5.1: A Chronology of Media Effects Paradigms Further reading: “Media effects Theories” , “Media effects” Table 5.2: Media Influence Functions
Table 5.2: Media Influence Functions - WORKSHOP #5:How did modern media change your life style?
- MEETING SIX: PROPAGANDA
- Definition: “Information, especially of a biased or misleading nature, used to promote a political cause or point of view.“Key words: information, disinformation, misinformation, infomediary, advertise, ideology, demagoguery, bias, persuasion, censorship, hegemony, publicity, public relations, nationalism, agitprop, poster, leaflet, pamphlet, banner, slogan, campaign, satire, loaded language, lies, deception, hate, slander, falsehood, fallacy, falsity, junk, brainwashing, mouthpiece, slander, drivel, untruth, calumny, machination, cult, perfidy, subterfuge, sophistry, masquerade, caricature, rhetoric, smear, critique, parody, brinkmanship, crackdown, hearsay, newspeak, doublespeak, jingoism, brinkmanship, sloganeering, claptrap, disseminate, incite, denounce, brand (verb), indoctrinate, inculcate, mock, glorify, demonize, denounce, criticize, agitate, sensitize, denigrate, discredit, vilify, engage, vilify, provoke, incite, critique, parody, vitriolic, gerundive, malicious, subjective, proactive, reactionary, provocative,Task: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it means.Academic media scholars like Noam Chomsky consider mass media as a distorting lens that represents the vested interests of economic elite/ruling classes.Mass media decide (through propaganda) what the public is allowed to see, hear and think about. “Systematic propaganda”: Through messages and symbols, the mass media do not only amuse, entertain and inform individuals, but also inculcate them with values, beliefs, and codes of behavior.Chomsky speaks of filters to explain how this is done (See Powerpoint 6.1 below! and Youtube Video #2 further down!!).PPP 6.1: Propaganda Model

- WORKSHOP #6:
- In George Orwell’s Animal Farm, we first encounter propaganda through the character of ___________.Old Major, Snowball, Napoleon, Squealer
- In George Orwell’s Animal Farm, which of the following is a propaganda technique employed by Old Major? Rewriting history, Inventing statistics, Use of slogans, Appeal to authority
- In George Orwell’s Animal Farm, which of the following is a symbol used as propaganda for the Animalism movement? Old Major’s skull, Old Major’s war ribbons, Jones’ pitchfork, The horses’ old harnesses

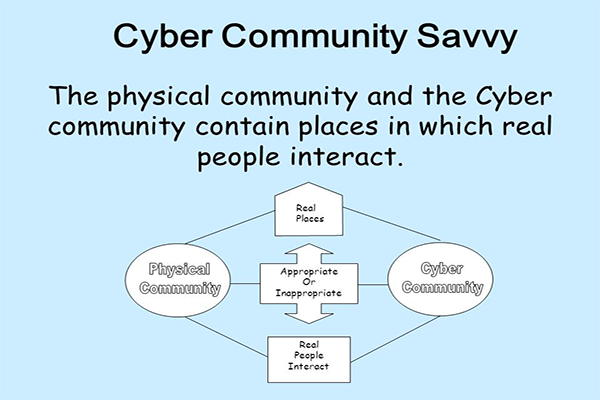
- MEETING SEVEN: CYBERSPACEDefinition: “Virtual reality.“CYBER: A combining form meaning “computer,” “computer network,” or “virtual reality,” used in the formation of compound words such as “cyberfashion”.Key words:internet, intranet, extranet, telnetcomputer network, computerize, computational, compute, computable, anticomputer, precomputer, computerology, neurocomputer, computerologist, computernik, nanocomputer, computerdom, telecomputer, biocomputing, minicomputer, microcomputercybernetic, cyberspace, cybercrime, cybertechnology, cybersociology, cybernetics, cybersavvy, cyberjargon, cyberjunkie, cyberinteraction, cybernetwork, cybersystem, cyberpsychology, cyberphilosophy, cyberterrorism, supercomputer, telecommuter, cybersuicide, cyberintrusion, cybergeneration, cyberinformation, cyberfuture, cyberdating, cybereducation, cyberpatient, cyberage, cyberia, cyberimmortality, cyberbullying, cyberslang, cybrarian, cybercitizenantivirus, teleprocessing, uploader, pseudocode, hackathon, incrementor, techie, darknet, rootkit, metaprogramming, microprocessor, content management system (CMS), visual display unit, digitized, hackers, phishing, malware, bots, spam, spamming, piracy, firewalls,Task: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it means.Cybercommunity: Cyberspace is home to thousands of groups of people (Virtual communities) who meet (in places called websites) to share information, discuss mutual interests, play games and carry out business.
 WORKSHOP #7:Discuss what sets off a virtual community from its real life counterpart.
WORKSHOP #7:Discuss what sets off a virtual community from its real life counterpart. - MEETING EIGHT: ADVERTISINGDefinition: “A means of communication with the users of a product or service.” Advertisements/Adverts/Ads are messages paid for by those who send them and are intended to inform or influence people who receive them.Advertisers use media to get their message across. They do this via television, print (newspapers, magazines, journals, etc), radio, press, internet, direct selling, hoardings, mailers, contests, sponsorships, posters, clothes, events, colours, sounds, visuals and people (endorsements).Advertising is made up of companies that advertise, agencies that create the advertisements, media that carries the ads, and people like copy editors, visualizers, brand managers, researchers, and designers. Key words:Ad Completion, Ad Fraud, Ad Network, Ad Server, Ad Tech, Agency Trading Desk, Audience Extension, Behavioral Targeting, Bot, Brand Lift, Connected TV, Contextual Targeting, CPC (Cost per Click), CPCV, (Cost per Completed View), CPE (Cost per Engagement), CPI (Cost Per Install), CPM (Cost per Thousand), CPV (Cost per View), Cross-Channel, CTR (Click-Through Rate), Data Management Platform (DMP), Daypart, Primetime, Deal ID, Display Advertising, DMA (Designated Market Area), DOOH (Digital Out-Of-Home advertising), DSP (Demand-Side Platform), DIA (Dynamic Ad Insertion), eCPM (Effective Cost per Thousand), Fill Rate, First-Party Data, Frequency, Geotargeting, GRP, Hashing, In-Stream, Insertion, Insertion Order, Interactive In-App Pre-Roll, Interactive Pre-Roll, KPI (Key Performance Indicator), Linear TV, Makegoods, Message Recall, Mid-Roll, Mobile Pre-Roll, MRC (The Media Rating Council), Open Exchange, Opt In, OTT (Over-the-Top), SVOD (Subscription Video-on-Demand), Page Request, PII (Personally Identifiable Information), Pixel, Post-Roll Ad, Pre-Roll Ad, Programmatic Ad Buying, Programmatic Direct, Programmatic Non-Reserved, Programmatic TV (PTV), Real-Time Bidding (RTB), Retargeting (Remarketing), RON (Run-of-Network), ROS (Run-of-Site), Second-Party Data, Sell-Through Rate, Set-Top Box, Share of Voice (SOV), Skippable Pre-Roll, Skyscraper, SSP (Supply-Side Platform), Standard Pre-Roll, Target Audience, Third-Party Ad Server, Third-Party Data, Unique User/Device ID, VAST (Video Ad Serving Template), vCPM (Viewable CPM), Viewability, Viewable Completion, Viewable Impression, VPAID, (Video Player Ad-Serving Interface Definition), VTR (View-Through Rate), Yield (Ad click rate),Yield ManagementTask: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it means.
 WORKSHOP #8:Consider instances of overt (open) vs covert (hidden) messages in advertising.
WORKSHOP #8:Consider instances of overt (open) vs covert (hidden) messages in advertising. - MEETING NINE: SOCIAL MEDIADefinition: “Any Internet website, smartphone application, or other modern technology that allows people to connect with one another and build online communities.“There are many forms of social media, including blogs, micro-blogs, wikis, social networking sites, photo-sharing sites, instant messaging, video-sharing sites, podcasts, widgets, virtual worlds, and more.Facebook/Twitter/Instagram are some of the most popular social media today.Advantages of Social Networking:On a personal level, social media allows you to communicate with friends and family, learn new things, develop your interests, and be entertained. On a professional level, you can use social media to broaden your knowledge in a particular field and build your professional network by connecting with other professionals in your industry. At the company level, social media allows you to have a conversation with your audience, gain customer feedback, and elevate your brand.Disadvantages of Social Networking: Lacks emotional connection; Gives people a license to be hurtful; Decreases face-to-face communication skills; Conveys inauthentic expression of feelings; Diminishes understanding and thoughtfulness; Causes face-to-face interactions to feel disconnected; Facilitates laziness; Creates a skewed self-image; Reduces family closeness; Causes distractions.Key words:A/B testing, Ads Manager, Algorithm, Analytics, Application Programming Interface (API), Audience, Avatar, Average response time, Business-to-Business (B2B), Business-to-Consumer (B2C), Bio, Boosted post, Brand advocate, Brand awareness, Business Manager, Chatbot, Clickbait, Clickthrough rate (CTR), Conversion rate (CVR), Cost per click (CPC), Cost per mille (CPM), Crisis management, Cross-channel, Crowdsourcing, Dark post, Dark social, Direct message (DM), Disappearing content, Employee advocacy, Engagement rate, Evergreen content, Feed, Follower, FOMO, Frequency, Geotargeting, Hashtag, Header image, Impressions, Key performance indicator (KPI), Listicle, Meme, Metric, Native advertising, Newsjacking, Objectives, Pay per click (PPC)Platform, Reach, Relevance score, Retargeting, Sentiment analysis, Shareable content, Social customer service, Social listening, Social media monitoring, Social media ROI, Social selling, Targeting, Traffic, Trending topic, User generated content (UGC), Vanity metric, ViralTask: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it stands for.
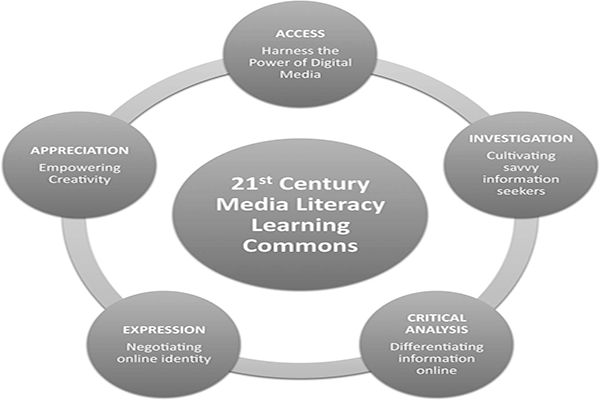
 Recommended viewing: The Social Dilemma (Documentary)WORKSHOP #9:Why are social media so addictive?MEETING TEN: MEDIA LITERACYDefinition: “The ability to access, analyze, evaluate and create media in a variety of forms.”Media influences our culture. Media is our culture.Hence the necessity to adopt a new approach to education: “Media Literacy”. Media literacy helps learners acquire the ability to:Access: The ability to reach/create media on the part of consumers: to respond to the dominant media, for example. Analyze: The ability to undestand the smallest details involved in media texts such as design, images and language.Evaluate: The ability to critique and ask relevant questions about various aspects of media such as agenda, goals and message.Create: The ability to skillfully produce media and target/manipulate audiences.Key words:Note: Some of the Media Literacy terminology mentioned here may overlap with key terms for the previous 9 Media Studies meetings (above). After all, Media Literacy encopasses all of the aforementioned.Agenda-setting, Bias, Branding, Censorship, Confirmation bias, connotation, Consumers, Copyright, Critical thinking, Deconstruction, Demographics, Fair use, Fake news, Freedom of expression, Gatekeepers, General Data Protection, Regulation, Genre, Hegemony, HTML, Imagined Communities, Intertextuality, Manufacture of consent, Marketing, Mass media, Media (medium), Media Literacy, Media ownership, Media pluralism, Media specialist, Metadata, Personal data, Product placement, Propaganda, Psychographics, Remix, Representation, Right to be forgotten, Right to privacy, Stereotype, Subtext, Text, Transparency, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Visual literacy.Task: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it means.
Recommended viewing: The Social Dilemma (Documentary)WORKSHOP #9:Why are social media so addictive?MEETING TEN: MEDIA LITERACYDefinition: “The ability to access, analyze, evaluate and create media in a variety of forms.”Media influences our culture. Media is our culture.Hence the necessity to adopt a new approach to education: “Media Literacy”. Media literacy helps learners acquire the ability to:Access: The ability to reach/create media on the part of consumers: to respond to the dominant media, for example. Analyze: The ability to undestand the smallest details involved in media texts such as design, images and language.Evaluate: The ability to critique and ask relevant questions about various aspects of media such as agenda, goals and message.Create: The ability to skillfully produce media and target/manipulate audiences.Key words:Note: Some of the Media Literacy terminology mentioned here may overlap with key terms for the previous 9 Media Studies meetings (above). After all, Media Literacy encopasses all of the aforementioned.Agenda-setting, Bias, Branding, Censorship, Confirmation bias, connotation, Consumers, Copyright, Critical thinking, Deconstruction, Demographics, Fair use, Fake news, Freedom of expression, Gatekeepers, General Data Protection, Regulation, Genre, Hegemony, HTML, Imagined Communities, Intertextuality, Manufacture of consent, Marketing, Mass media, Media (medium), Media Literacy, Media ownership, Media pluralism, Media specialist, Metadata, Personal data, Product placement, Propaganda, Psychographics, Remix, Representation, Right to be forgotten, Right to privacy, Stereotype, Subtext, Text, Transparency, Universal Declaration of Human Rights, Visual literacy.Task: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it means. WORKSHOP #10:Discuss the contrast between a media literate and a media illiterate person.
WORKSHOP #10:Discuss the contrast between a media literate and a media illiterate person.
- MEETING SEVEN: CYBERSPACEDefinition: “Virtual reality.“CYBER: A combining form meaning “computer,” “computer network,” or “virtual reality,” used in the formation of compound words such as “cyberfashion”.Key words:internet, intranet, extranet, telnetcomputer network, computerize, computational, compute, computable, anticomputer, precomputer, computerology, neurocomputer, computerologist, computernik, nanocomputer, computerdom, telecomputer, biocomputing, minicomputer, microcomputercybernetic, cyberspace, cybercrime, cybertechnology, cybersociology, cybernetics, cybersavvy, cyberjargon, cyberjunkie, cyberinteraction, cybernetwork, cybersystem, cyberpsychology, cyberphilosophy, cyberterrorism, supercomputer, telecommuter, cybersuicide, cyberintrusion, cybergeneration, cyberinformation, cyberfuture, cyberdating, cybereducation, cyberpatient, cyberage, cyberia, cyberimmortality, cyberbullying, cyberslang, cybrarian, cybercitizenantivirus, teleprocessing, uploader, pseudocode, hackathon, incrementor, techie, darknet, rootkit, metaprogramming, microprocessor, content management system (CMS), visual display unit, digitized, hackers, phishing, malware, bots, spam, spamming, piracy, firewalls,Task: Look up each of the above key terms and make sure you know what it means.Cybercommunity: Cyberspace is home to thousands of groups of people (Virtual communities) who meet (in places called websites) to share information, discuss mutual interests, play games and carry out business.
Reading List
Viewing
-
- Assignment #1Choose a TEXT and discuss it in terms of “representation”, “identity”, “production”, “consumption” and “regulation”.
- Assignment #2Design an appropriate plan for a particular product (of your own choosing) with a specific audience in mind.
- Assignment #3 Pick a cyber-community and compare it with its counterpart in real life.
- Assignment #4 View Chomsky’s video “Manufacturing Consent” (link above!) and answer the following questions: What is the movie about? Provide 3 alternative titles. Mention 3 key ideas from the movie.
- Assignment #5 Why is social media so addictive? (Use Youtube video #3 above!)
- Assignment #6Consider the following: “Steps you would take to limit the negative effects of mass media.”
- Assignment #7Respond to the following question: “How do you picture the future of modern media?”
- Deadine for assignments is May 20th!
- Deadine for assignments is extended to June 20th!
- NOTE: Papers should be no less than 5 paragraphs in length. Files should be sent by e-mail as a word document and clearly marked as Full-Name_Media-assignment#1.docx. PDF files will not be processed. Refer to the paper submission guidelines at the bottom of this page. Prior to posting here, the questions/statements for assignments are discussed during in-class workshops.
Useful Links
Journal of Media and Communication Studies
-
-
Final Exam
Media Studies written Final will take place at these times:
Date: (…)
Time: (…)
Venue: (…)
N.B.: Be on time. Bring your student ID card and the invitation to take the exam.
-
Make-Up Exam
Media Studies written Make-up will take place at these times:
Date: (…)
Time: (…)
Venue: (…)
N.B.: Be on time. Bring your student ID card and the invitation to take the exam.
-
END-OF-TERM PAPERS

Reading List
FULL LIST OF METHODOLOGY BOOKS
Internet Search: Tips
Research Gap

How to Identify a Research Gap? – May 28, 2020
Assignment
Read this year’s on “Topic” and prepare any questions you may have for our 1st meeting. Choose an appropriate title. Write an outline. Refer to the paper submission guidelines at the bottom of this page.
Contact
Use the End-of-Term Project CONTACT FORM for any questions you may have about your research paper.
-
- A seminar will take place on Tuesday 2nd of April, 2024 starting 12:00pm in Lab 1 across from the department.
- For our meeting on Tuesday try and bring along the following:
- 1. Your chosen topic
- 2. Research question/s (Your paper will attempt to answer that/those question/s!)
- 3. An Outline
- 4. Any general questions you may have
Link
Many of you are having an issue with lined up lines for the TABLE OF CONTENTS. Here is a youtube that shows you how to Create Lines in Word with Tabs.
Deadline
Completed papers (electronic copy – sent by e-mail) should be submitted by May 25th 2024.
Completed papers (hard copy – handed in at the Department) should be submitted by June 30th 2024.
Cover page for hard copies have been standardized. A sample can be downloaded here: COVER PAGE SAMPLE
IMPORTANT NOTE
Make sure you read the submission guidelines (Find the link at the bottom of this page!) before submitting your work.
Papers will be returned uncorrected in these two cases:
1. NOT FULLY PROOFREAD (Proofread & Resubmit !). 2. PDF FORMAT (Resubmit as a Word document !).
STUDENT CORRESPONDENCE

Students in Dr Bouzidi’s class (S3&S4) and End-of-term papers group (S6) need to fill out the to receive notification e-mails.
-
- List of students (End-of-Term Papers/#S62022/Prof. Bouzidi | G2) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Media Studies/#S42022/G7+G8) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Public Speaking/#S32021/G7+G8) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (End-of-Term Papers/#S62021/Prof. Bouzidi’s group) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Media Studies/#S42021/G7+G8) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Public Speaking/#S32020/G7+G8) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (End-of-Term Papers/#S62020/Prof. Bouzidi’s group) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Media Studies/#S42020/G1+G2) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Public Speaking/#S32019/G3+G4) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (End-of-Term Papers/#S62019/Prof. Bouzidi’s group) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Media Studies/#S42019/G1+G2) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Public Speaking/#S32018/G1+G2) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (End-of-Term Papers/#S62018/Prof. Bouzidi’s group) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Studies in Media/#S42018/G1+G2) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Public Speaking/#S32017/G3+G4) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (End-of-Term Papers/#S62017/Prof. Bouzidi’s group) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Studies in Media/#S42017/G7+G8) registered for notification e-mails.
- List of students (Public Speaking/#S32016/G9+G10) registered for notification e-mails.
Students should submit their papers via the .
Make sure you read the carefully before you submit your paper.
Contact
Use the End-of-Term papers CONTACT FORM for any questions you may have about your research paper.